- 9+1=10, WMU's Environment/Ecology ranks among the top 1% of ESI worldwide
- Author:Graduate School Date:November 27, 2023
Recently, Clarivate has released the latest ESI rankings. The discipline of Environment/Ecology of WMU has newly entered the top 1% of ESI global rankings, marking a new stage of WMU’s discipline construction.
Public Health & Preventive Medicine is the main supporting discipline of Environment/Ecology at WMU. Relying on the National Health Commission Key Laboratory of Radiobiology and the Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Watershed Sciences and Health, this discipline mainly conducts scientific research on the epidemiology of non-communicable diseases, the mechanism of health damage caused by ionizing radiation, the toxic effects and mechanisms of environmental pollutants, as well as population health risk assessment, and nutrition and health. The discipline has established four specializations: Epidemiology and Health Statistics, Occupational and Environmental Health, Nutrition and Food Hygiene, and Health Toxicology.
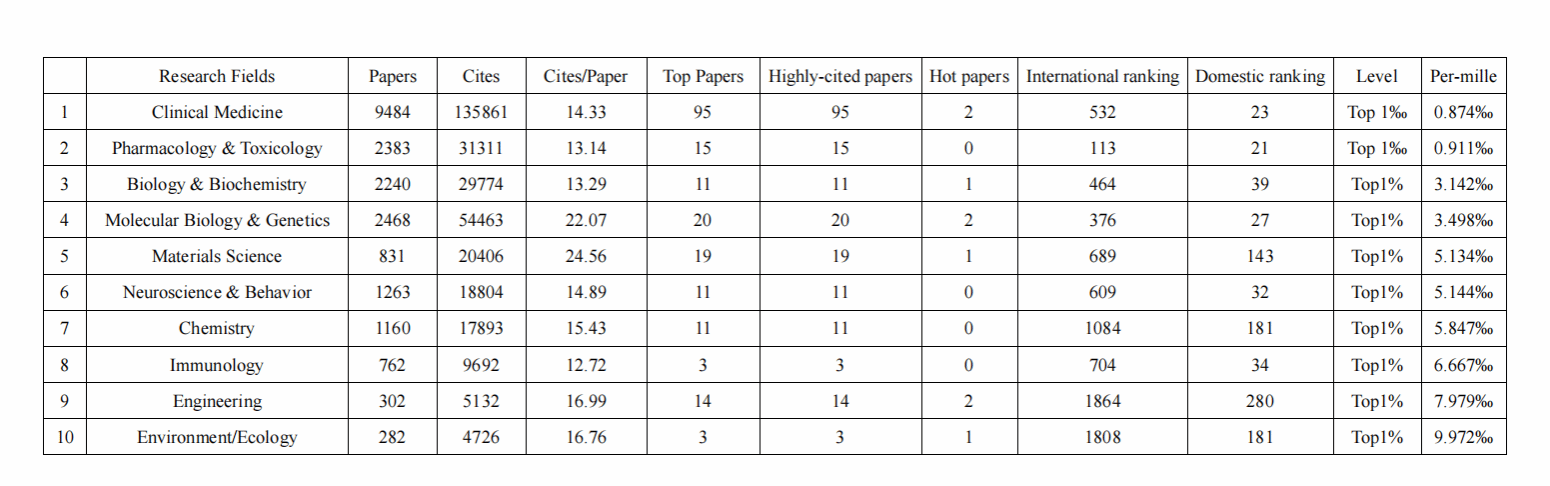
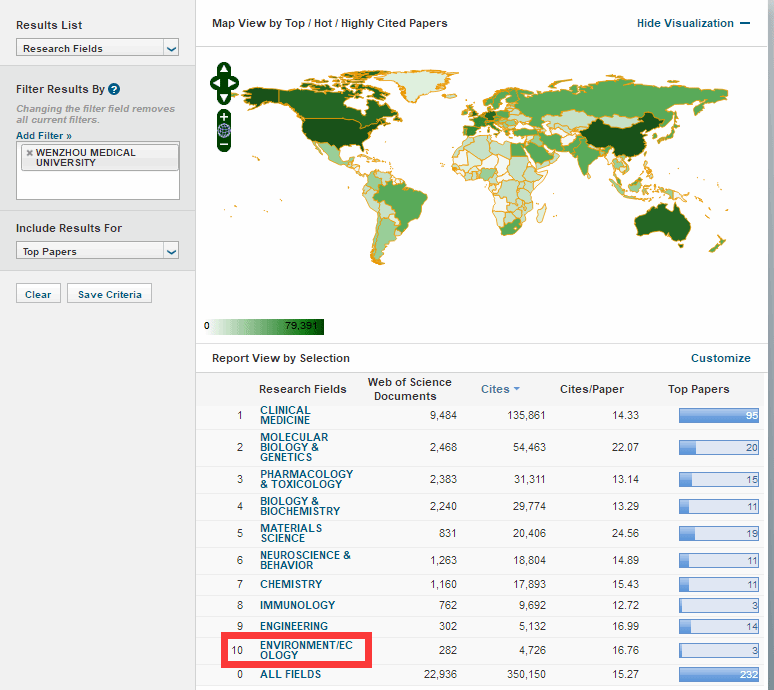
Up to now, 10 disciplines of our university have entered the top 1% of ESI global rankings, of which Clinical Medicine and Pharmacology & Toxicology have entered the top 1‰. WMU ranks 735th among 8,917 listed institutions in the world and 70th among domestic institutions, making the university the second among provincial universities and fifth among independent medical universities. The discipline of Clinical Medicine ranks top 0.874‰ in the ESI global rankings, Pharmacology & Toxicology ranks top 0.911‰ in the ESI global ranking, and the rankings of other disciplines have significantly improved.
In recent years, the university has taken the construction of first-class disciplines as the guide to promote the construction of a high-level university. Focusing on the major strategic needs of the country and the frontiers of scientific and technological development in the world, the university has carried out scientific research around biopharmaceutics and optometry, and actively promoted the construction of the discipline group of emergency and critical care, and tissue and organ regeneration and repair, as well as the discipline group of ophthalmology & optometry. In addition, the university has deepened the substantive cooperation of clinical medicine with engineering, science, and humanity, strengthened multidisciplinary collaborative research, guided its affiliated hospitals to build a scientific research collaborative development system focusing on solving clinical problems, and utilized the top disciplines to drive the development of the advantageous disciplines. Through continuous improvement of the discipline construction system and mechanism, the university has gradually manifested its discipline characteristics and advantages, and significantly built up the overall strength of all disciplines.
Essential Science Indicators (ESI) is a basic analysis and evaluation tool for measuring scientific research performance and tracking scientific development trends. It is a quantitative analysis database based on more than 10 million literature records from more than 12,000 academic journals worldwide included in Clarivate (formerly Thomson Reuters) Web of Science (SCIE/SSCI). ESI divides all sciences into 22 research fields. ESI has become one of the important evaluation index tools widely used in the world to evaluate the international academic level and influence of universities, academic institutions, and countries/regions. Disciplines listed in the top 1% of ESI are generally considered to be internationally high-level disciplines, and those in the top 1‰ are generally considered as top-ranking disciplines.
Text translated by Cai Lingchen and reviewed by Sun You
